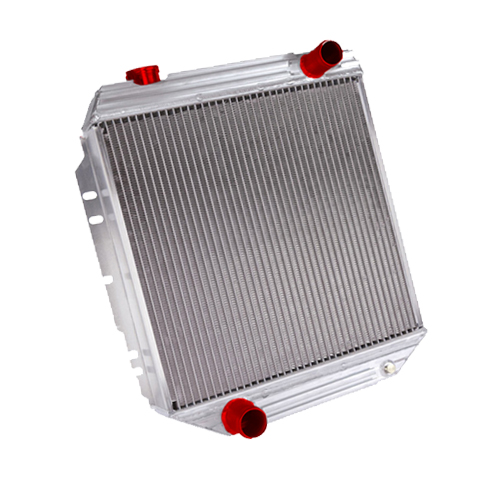
Radiators are heat exchangers used for cooling internal combustion engines, mainly in automobiles but also in piston-engined aircraft, railway locomotives, motorcycles, stationary generating plant or any similar use of such an engine.
Internal combustion engines are often cooled by circulating a liquid called engine coolant through the engine block, where it is heated, then through a radiator where it loses heat to the atmosphere, and then returned to the engine. Engine coolant is usually water-based, but may also be oil. It is common to employ a water pump to force the engine coolant to circulate, and also for an axial fan to force air through the radiator.